What is a #1 Google Ranking Worth?
Find this article useful? Please add this to del.icio.us for your future reference
This article is also available in German.
Sections
- An Example of Applying This Data to a Live Business Scenario
- Google Rankings Can Make or Break a Business
- Appreciating Google's Market Domination
- Establish a Baseline Keyword Value
- Typical Click Distribution Profiles
- Factors Modifying Click Distribution
- Tapping the Keyword Tail
- Improving Monetization via Scale
- Improve Your SEO Strategy Today
An Example of This Research in Action
Patrick, a moderator on our community forums, runs a Bingo Card Creator website which recently ranked #5 in Google for bingo cards.
- A #5 ranking sent him 6,000 unique visitors per month.
- A #1 spot, using the leaked AOL search data (referenced later in this document), is worth 8.5 times what #5 is. 6,000 * 8.5 = ~50,000 uniques per month
- His site currently makes $40 for every 1,000 pageviews.
- His estimated income from ranking #1 for [bingo cards]: $2,000 a month.
You could do this type of calculation for any keyword you rank for that has significant search volume. You can use some of the other data points listed below to create similar calculations - even if you do not rank yet.
Google Rankings Can Make or Break a Business
While perusing the web I came across a WebmasterWorld thread about how Google allows other webmasters to damage your rankings. A WMW member nicknamed Hissingsid stated
Sabotage is a serious problem and the more that Google's spam team seems to do the worse it seems to get. The damage doesn't have to be that big to have a massive effect on your site's performance. In our market even a 3 place drop can ruin your business.
It is scary to think how reliant many businesses have become on search, but search is big business. Google pulled in $5.19 billion in revenues in the 1st quarter of 2008, with $3.40 billion from Google's websites. Advertisers would not spend that much unless they profit from it.
How Much Are the Search Results Worth to Google?
Not once, but twice Google has accidentally publicly displayed values on their search results. But unfortunately both times the values were encoded and we can't see that data all the time.
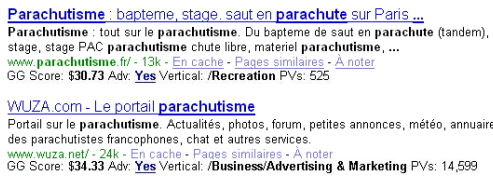

Unfortunately the only data points Google share with marketers are
- the price they charged you for a click
- how many clicks they sold you
- any conversion data you decide to share with them
- rough estimates of click value via their Traffic Estimator tool
You only get those first 3 AFTER you are charged for the traffic, and the fourth offers rough estimates which are likely to be wildly off unless you understand their various ad matching types and normalize the data.
Putting the Value of SEO in Context
As large as Google's revenues are, more searchers click on the free / organic search results than the paid ads. With that in mind, I thought it would be fun and rewarding to create a guide to estimate the value of ranking for particular keywords in major search engines for 3 reasons:
- to raise awareness of the importance and value of SEO
- to help motivate businesses and individuals to optimize their web presence
- to encourage top ranked websites to improve the quality of their sites in an attempt to protect and improve upon their current rankings (and thus improve the quality of the web as a whole)
Appreciating Google's Market Domination
U.S. Search Market
As shown in this image from Search Engine Land, most internet traffic rating services show Google to have 60% to 70% of the U.S. search market.
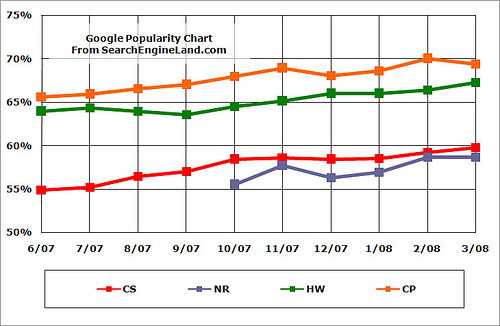
(CP = Compete.com, CS = Comscore, HW = Hitwise, & NR = Nielsen//NetRatings)
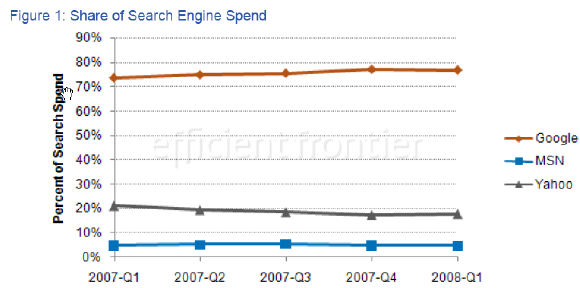
Given the above data, it is no surprise that advertiser spend at large SEM companies are aggressively focused on Google. Efficient Frontier's Q1 2008 data [PDF] shows that Google enjoys 77.2% of their client search ad spend.
Google Under-monetizes to Ensure Long Term Growth
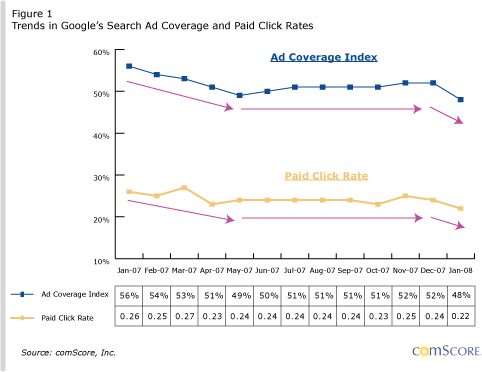
Google is less comprehensive with ad coverage than competing services. When Google choses not to display ads they are not maximizing short term revenues. This Comscore research shows that Google is being selective with when they display ads - only showing them when relevancy is strong.
Holding their advertisers to higher minimum bids and higher relevancy standards shows that Google is intentionally foregoing short term revenues to ensure longterm growth, which makes their current market domination even more impressive.
International Market Domination
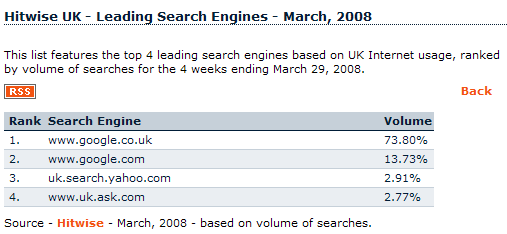
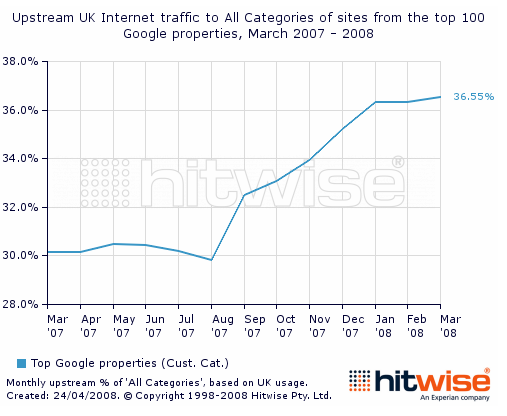
In many international markets, that domination is more fierce. In the UK Google not only has nearly 90% of the search market, but - according to Hitwise - Google controls a full 36.55% of the traffic going to UK websites. And, due to how search works, that 36.55% of traffic is generally more targeted and more valuable than the remaining pool of traffic.
The 2007 Global Search Report shows that Google dominates most European and Asian countries. Google leads the market in most countries in the report - with the exceptions of China, Czech Republic, Estonia, Japan, Russia, and South Korea.
Mobile Search Domination
Google's secret Android contracts require manufacturers to bundle Google as the default search service on the device & Google pays Apple over $1 billion per year to be the default search provider on iOS. In many markets Google has a mobile search marketshare above 96%.
Step 1: Establishing a Baseline Keyword Value
Given a fairly constant ranking position and traffic stream you should be able to estimate visitor value AND how much additional value would be created by improving your rankings. If you are not yet tracking your traffic and conversion trends you have a few options:
- Use analytics tools to start tracking your traffic and conversions.
- If you have a newer small site you may rank well in Microsoft prior to ranking well in Google. Google typically takes longer to rank in if you are starting from scratch.
- You can look at search marketshare numbers (from companies like Compete.com, Comscore, Hitwise, and Nielsen Netrating - reported monthly on Search Engine Land) to roughly estimate Google click volume based on how many clickthroughs you get from your Microsoft ranking.
- Set up an AdWords account, bid aggressively on appropriate keywords to ensure your ad gets strong distribution, and determine the value of a click based on tracking...
- your volume of traffic
- your conversion rate
- the average customer value (based on a metric like direct immediate ROI or lifetime customer value).
- Yahoo! offers a free ROI calculator to help you figure out how much you can afford to pay for traffic, and estimate your potential monthly profit or loss based on (search volume * cost per click * conversion rate * profit per conversion).
- Estimate the value of traffic based on tools offered from search engines, including the Google Traffic Estimator and Microsoft Ad Intelligence.
- The Google Traffic Estimator can be particularly rough because there are many variables that go into its calculations (including: bid price, ad CTR, quality score, etc.)
- This data can be refined by comparing new keywords against keywords you have ranked well for months or years.
- Microsoft Ad Intelligence offers top category keywords, and category based value estimates, though they have less traffic and a less efficient ad network than Google does.
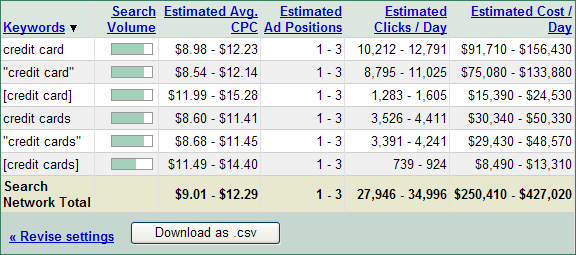
Sample Data from Google Traffic Estimator
If you leave the bid price blank while inserting your keywords in the Google Traffic Estimator, they will return click cost estimates and estimated clicks per day that are associated with ranking in the top ad position for 85% of relevant search queries.
Keep in mind that the value of these clicks depends on several major factors
- market competition - high volume and high value keywords are more efficient
- AdWords ad placement - if ads appear above the organic search results and are exceptionally relevant they can get a 10% to 30% clickthrough rate. Ads that appear on the side of the search results are typically much more likely to be clicked on ~ 1% of the time.
- language & country - settings like language and country help you control what market you are researching
- ad match type - Google offers 3 common ad matching types that control ad distribution, and 2 that help filter your ads from showing
Ads Above the Organic Search Results
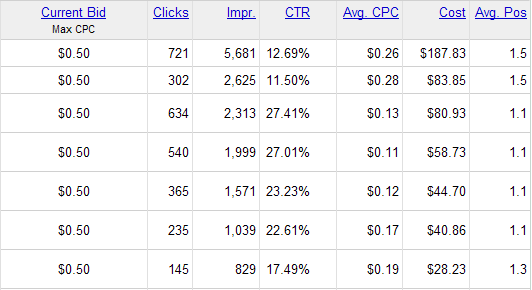
Here is a sample of click stats from a campaign spending a couple thousand dollars a month, where this ad is typically the only advertiser for the keywords, and the ads appear above the organic search results. Please note that for the keywords where the average ad position is 1.5 it is for broad match versions of the keyword, where there are competing advertisers for some search queries. Each row of data represents a different keyword.
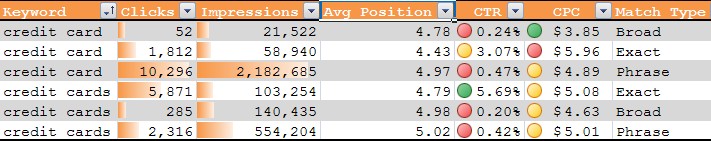
Sidebar Ads
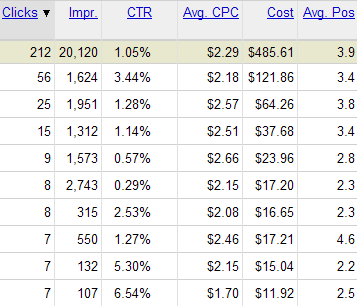
Here is a sample of data where the ads more commonly appear on the sidebar, though for a couple of the leading search queries in the group (those showing a 3% to 6% clickthrough rate) the ad sometimes appears on the top of the search results.
Accuracast Data
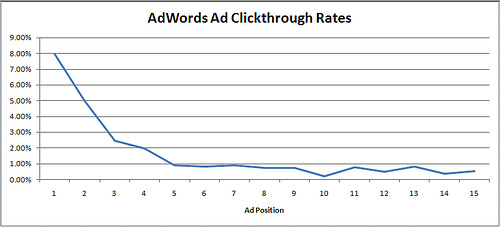
Accuracast shared their data on the CTR by ad position for over 1 million ad clicks.
Understanding Google AdWords (& Google Traffic Estimator) Keyword Match Types
- [exact match] - will show values for that specific keyword
- "phrase match" - will show values for searches containing that keyword (also includes exact match values)
- broad match - will show values for additional related keywords (includes exact match & phrase match values)
- negative match - this is used inside AdWords to prevent your ads from showing up. Google also has a match type called embedded match that less than 1% of advertisers probably use, and is beyond the scope of this document.
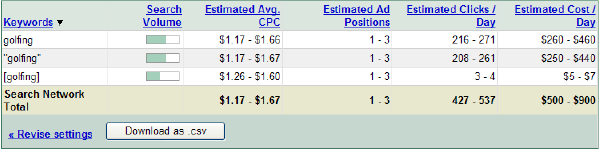
From my experience, depending on the commercial intent of the keyword, the number of advertisers appearing above the organic search results, and the user intent of a query you can multiply the Google Traffic Estimator numbers by about 4 to 7 to come up with traffic estimates that a #1 organic ranking would garner.
By default our keyword tool offers a convenient export option that generates exact match, phrase match, and broad match versions of keywords. We also offer a free keyword wrapping tool that allows you to wrap your keyword lists.
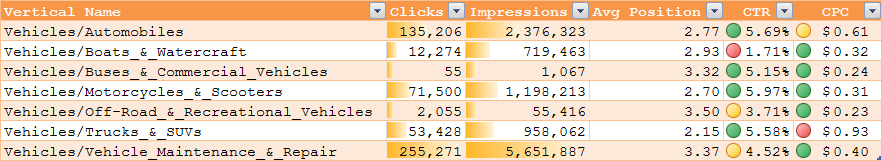
Sample Data from Microsoft Ad Intelligence
Microsoft Ad Intelligence offers a lot of free data. Here is a sample of top health insurance category keywords
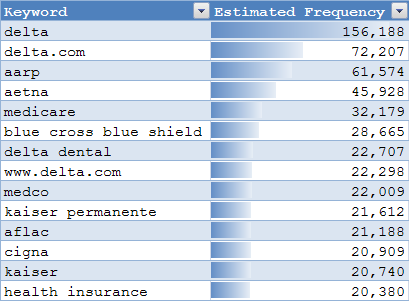
Here are Automotive Category KPIs - notice how the average cost per click is highest in the high margin trucks & SUVs category.
Step 2: Typical Click Distribution Profile
A friend recently said "whether we're 15 or 150 doesn't make much a difference." Indeed, search clicks are heavily concentrated on the top portion of the first page of search results. And this trend toward traffic consolidation has accelerated as time has passed.
AOL's Leaked Search Data
In August of 2006 AOL leaked millions of search records. Some SEOs scoured through this data to look at click data by ranking. A comment on Jim Boykin's blog reveals the percent of clicks for each position for 9,038,794 searches and 4,926,623 clicks. Donna Fontenot shared the relative click volume of lower ranked results relative to the top ranked site.
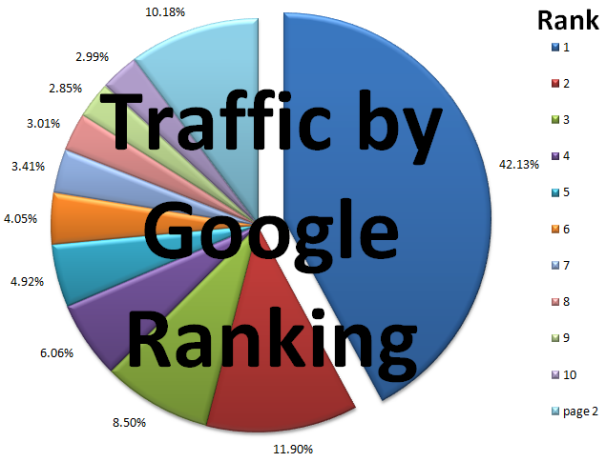
Overall Percent of Clicks |
Relative Click Volume |
|
|
1st page totals: 89.82%, 4,425,226 clicks |
|
Based on this data, if you are ranking 8, 9, or 10 you may be able to increase your traffic for that keyword 1,400% by ranking #1. Even jumping from #8 to #3 can triple your traffic.
Eye Tracking Research
Gord Hotchkiss put together 2 eye tracking studies showing how searchers interact with search results.
![]()
Notice the following
- how tightly Google keeps attention focused on the upper left corner of the search results
- how attention drops off the further down you go on the page
- ads in the right column generally do not get much attention
More Organic CTR Research
Here is an image from SEO Researcher highlighting the results of a much smaller eye tracking study by Cornell from 2004.
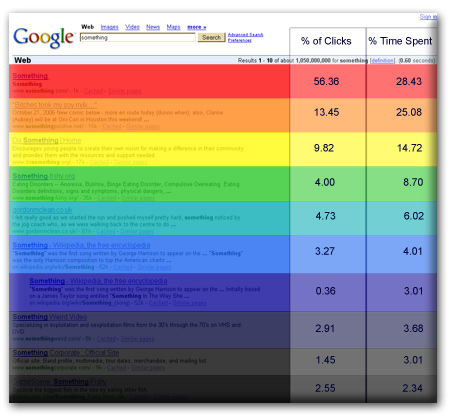
In May, 2010, ad network Chitika shared traffic stats coming into their network by Google ranking. It shows a similar profile to the leaked AOL data.
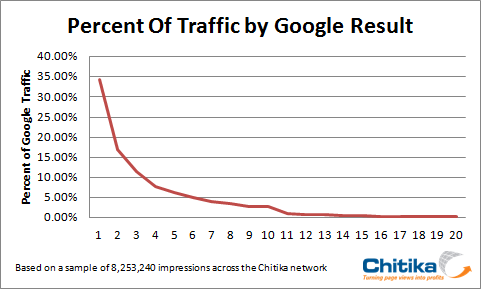
In December, 2010, Optify did a study of search traffic by ranking. It shows a similar profile to the leaked AOL data. In addition to showing the typical clickthrough rate data that other studies have shown, they also highlighted how keyword popularity and click price impact organic search clickthrough rates. For expensive keywords their data suggest a majority of the clicks go to AdWords ads, whereas on cheap keywords almost all the clicks go to the organic search results. On a per-keyword basis things like user intent & relevancy signals can further impact search click distribution.
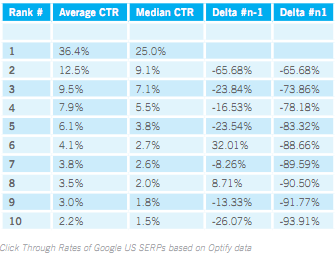
Slingshot SEO also created a SERP CTR curve.
AWR launched an interactive organic CTR curve using data from Google Webmaster Tools. It includes features for comparing clickthrough rates across keywords based on: search intent, category, the number of words in the search, branded vs unbranded queries, and variations on the number of ads on the result page. Sistrix also did a similar study.
NetBooster offers a CTR template in Excel which allows webmaster to analyze data exports from Google WMT to create their own CTR curve.
Analytics SEO analyzed raw data of CTR to generate scatter plots showing how large variation is in the data. They found that for sites ranking on many keywords, larger branded websites got a higher CTR when ranking highly on unbranded terms than smaller & lesser known sites do when ranking for the same keywords. They also found that keywords with lower impression counts tended to have flatter CTR curves, which might indicate searchers are visiting more results when they are looking for a specific longtail topic to find the precise information they need.
Internet Marketing Ninjas conducted a study of organic CTR in 2017 which highlighted how CTR varried across different query types.
| Position | Overall | B2C | B2B | Non-brand | Brand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.12% | 20.83% | 22.58% | 19.30% | 26.53% |
| 2 | 10.65% | 10.07% | 12.62% | 10.57% | 23.91% |
| 3 | 7.57% | 7.39% | 8.27% | 7.54% | 9.45% |
| 4 | 4.66% | 4.22% | 7.24% | 4.65% | 8.75% |
| 5 | 3.42% | 2.99% | 6.19% | 3.42% | 5.39% |
Google's search result layout shift that did away with right sidebar, which provided a strong lift in clicks on top of page ads (which means organic listing CTR suffered significantly).
| Position | Old CTR | New CTR | CTR Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.77% | 7.65% | 32.56% |
| 2 | 2.48% | 2.84% | 14.79% |
| 3 | 1.28% | 2.20% | 72.44% |
| 4 | 1.08% | 1.64% | 51.85% |
| 5 | 0.84% | 0.78% | -7.56% |
The thing to be aware of with the CTR curves is that they are generally illustrative, but they may not be precise for your website & your keywords. (If they were precise across the board then clearly more of the studies would line up exactly against each other in aggregate.)
Here are some examples of how keywords may be different. Some keywords:
- have 1 to 4 AdWords ads above the organic results (some of which ads may also have single-line sitelinks or multiple paragraph sitelinks under them, along with other ad extensions like click to call, reviews, ratings, etc.
- have product listing ads
- have a map, or a map with Hotel Ads
- have featured snippets
- have a knowledge graph
- have interactive elements like calculation utilities or sport stats
- have irrelevant ads and/or organic search results, which cause users to look deeper through the result set
- are primarily done on desktop devices, or are primarily done on mobile devices
- are brands, which have many people clicking on the official website listing (some brands are given a larger listing with multiple sitelinks in it)
- have graphical product ads in the search results
- are localized to rank local sites higher in some areas
- have results from Google verticals: Youtube videos, Google News, Google images, Google Product Search, Google Squared, flight data, etc.
- appear differently on different search engines, with not only different rankings, but also different ads & promotional pieces in and around the search results content area
Since every keyword is different, it is valuable to consider the CTR curves as generally illustrative, rather than a precise measure that is true across the board. If you want more granular data for your website, Google's Webmaster Tools provides aggregate CTR data per-keyword basis & CTR data based on ranking position.
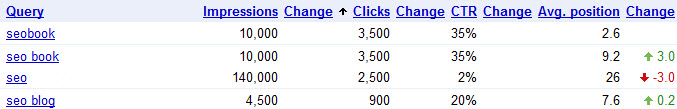
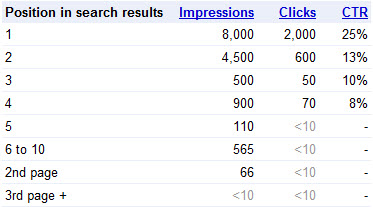
WMT Warnings
- Google's spam team have use WMT data for torching networks. If you run a network of thin affiliate sites or other grayhat SEO sites - this service is not for you.
- Google has been known to have various levels of transparency and accuracy with their data over time. Sometimes it is close to spot on & sometimes it is way off.
- If you have a double listing in the search results they may show your CTR as being half what it actually is (since they count that 1 search as 2 search impressions, so for our branded searches like "seo book" & "seobook" our CTR is closer to 70% to 85%, rather than the 35% shown above).
- Google's WMT data tends to only list data for a recent period of time. You either have to regularly export it or use a third party platform which does to keep track of historical data. Another way around this limitation is to use the paid vs organic report inside AdWords.
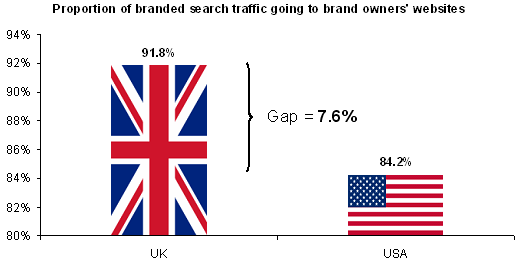
Organic Search Result Click Trends
A large part of the reason that the top listing gets so many clicks is because many searches are navigational / brand focused. Hitwise research shows over 80% of brand searches end up at the brand owners' website.
But even beyond that brand bias, there is a significant advantage to ranking #1 for other search queries. Jakob Nielsen wrote a 2005 column titled The Power of Defaults, in which he cited research showing...
- 42% of users clicked the top search result while 8% clicked the second listing.
- When the top two listings were swapped 34% of searchers still clicked the top listing and 12% clicked the second listing.
Since that point in time the power of defaults has only increased. Over the years the general trend is more searchers clicking listings on the first page with fewer clicks on the second page or subsequent search results. This 2008 iProspect report reveals how drastic this trend has been
| Year | 1st page | top 3 pages | > 3 pages |
| 2002 | 48% | 81% | 19% |
| 2004 | 60% | 87% | 13% |
| 2006 | 62% | 90% | 10% |
| 2008 | 68% | 92% | 8% |
From my experiences those iProspect search habbits skew a bit low, and a blog post from May of 2008 by Enquisite shows nearly 90% of searchers click on the first page of search results. Their data also includes image results, so the consolidation of traffic on the first page of text search results might be even greater than represented in their overall data sample.
As search grows more sophisticated, the web grows to offer more quality signals, search companies collect more usage data, and we grow more accustomed to search the trend of clicking high on the first page is likely to accelerate at an even faster pace.
Pay Per Click Ad CTR Research
In 2004, Atlas DMT shared data about how ad rank affects the clickthrough rate of their clients Google AdWords and Overture ads.
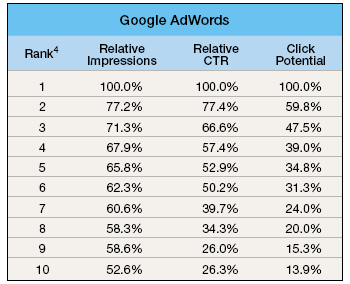
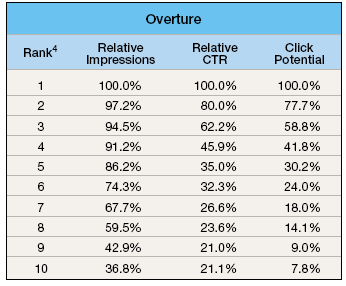
Since 2004 all major PPC networks have got more aggressive at implementing quality scores. Throughout 2007 Google tightened down on quality scores to show fewer ads across fewer search queries, which has had the effect of giving greater weight to the top ranked ads and lowering the opportunity to buy cheap ads where relevancy is limited.
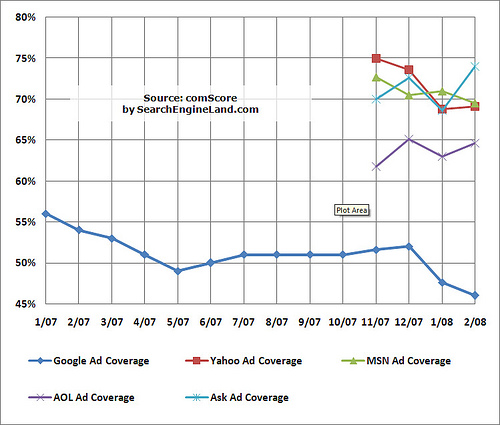
Some of the other search engines show ads across a much larger percentage of their overall search queries, as showing in this chart from Search Engine Land.
Comparing Organic Search Clicks to PPC Clicks
Conversion Rates Are Roughly Equal
A 2004 MarketingSherpa survey of 3,007 marketers highlighted that paid search works slightly better for B2B oriented offers, while organic search works better for B2C offers.
Survey results revealed that much depends on what your target demographic is and what your conversion action is. So, b-to-b marketers seeking lead generation wound up with 7.6% conversions from paid search versus 6.7% conversions from organic clicks. On the other hand, b-to-c ecommerce sites with an average sale of $51-100 converted 4.8% of paid search clicks to buyers versus 6.5% of organic clicks.
A 2006 WebSideStory study gave paid search a slight edge on B2C ecommerce sites, stating that paid conversion rates favored organic search rates 3.4% to 3.13%.
Organic Search Gets More Click Volume
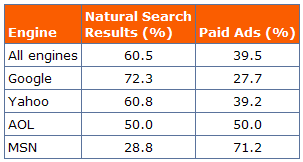
A 2004 iProspect study [PDF] showed the clickthrough rates at the major engines for organic vs paid search results
Please note that a large part of that data skew for Microsoft was because they used LookSmart, which was far more aggressive with ad placement than current search engines are.
- In 2004 at the New York Search Engine Strategies conference a JupiterMedia analyst stated that 5 out of 6 commercial purchases which originated from search originated from the organic search results. They also stated "algorithmic listings in search indexes generate an estimated six in seven commercially natured search referrals."
- In early 2008 Google's Avinash Kaushik stated that 14% of Google clicks are on paid search ad and 86% of clicks are on organic search results.
- 2008 Penn State research titled Determining the informational, navigational and transactional intent of Web queries [PDF] found that roughly 80% of search queries were informational, while approximately 10% were each navigational and transactional. With so many searches being informational and navigational, it is unsurprising that people click the organic search results more often than the associated PPC ads.
Using Competitive Research Tools to Estimate Click Distribution
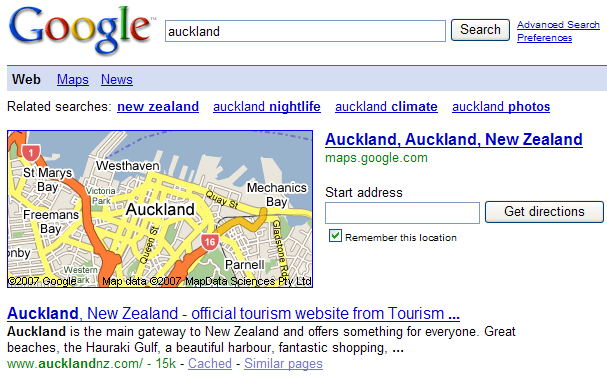
Compete.com Search Analytics allows you to view the top 5 destinations for the exact match version of a keyword for free, and offers further data if you subscribe to their paid service.
For the keyword credit cards you can search Google to see what the search results look like, and look at Compete.com's keyword destination results. Notice how Compete.com shows the keyword share that each site gets...that is the percentage of the search traffic from that keyword that they are capturing. This is exceptionally useful if you already rank in the search results and want to see how much lift a better ranking might bring.
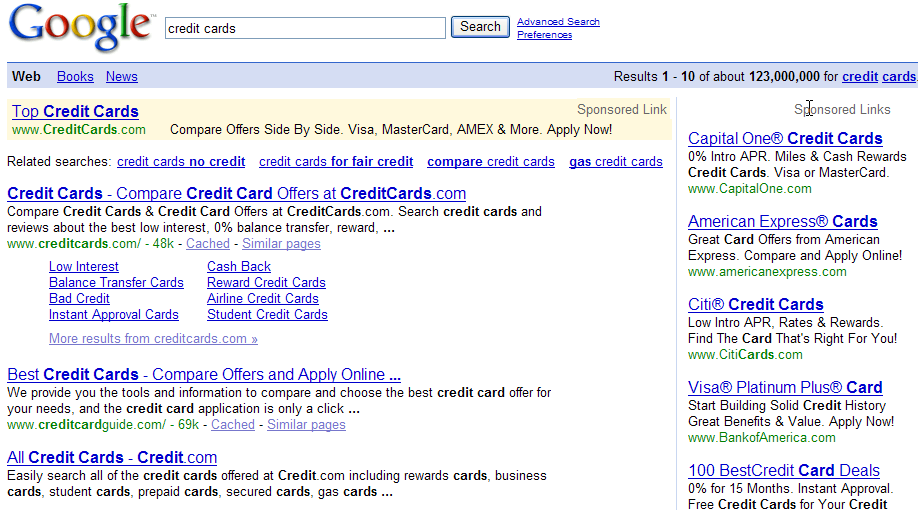
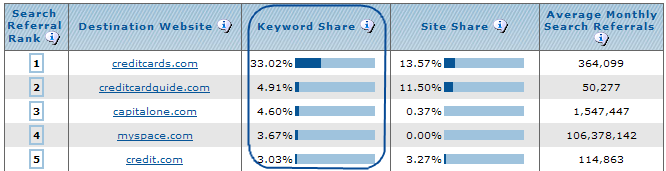
* Due to their limited sample size this strategy is only effective for high volume keywords. I believe Compete.com data is currently focused on United States based searchers, though they were recently purchased and are looking to expand their offering.
If search results have changed over time, that may also throw off the ability to pull meaningful click distribution data from the current search rankings, but many of the highest value keywords are fairly stable, largely because many are based on large volumes link equity.
Wikipedia Shares Their Stats for Free!
Google ranks Wikipedia content across a wide array of keywords. This website allows you to see how many pageviews each Wikipedia page gets, and lists the top 1,000 pages, here is a random sample of that data.

Many of these pageviews are driven by Google organic search rankings. Tie this sample data in with the leaked AOL search data referenced above, and for any Wikipedia page that ranks well in Google you should have a good idea of the potential traffic in that space.
Because of it's encyclopedic nature, each Wikipedia page can rank for a broad basket of related keywords rather than ranking for just a single keyword - so you can think of the Wikipedia stats as being similar to the traffic totals for a group of related broad matched keywords.
Step 3: Factors That Modify Click Distribution
A variety of factors must be taken in account for when estimating overall search volume distribution. While this list is not exhaustive, it contains many of the common factors worth considering. Whenever possible we also offer tips for how to overcome these data biases.
- brand - if people are looking for a specific brand or intend to go to another location it is hard to outrank the core brand and hard to be perceived as being more relevant or clickworthy
- user intent & information scent - some users research while others are looking to buy.
- paid search ads - if paid ads appear above the organic search results they drive down the organic listings
- sitelinks, subdomains, & multiple listings - Google gives some top ranked sites up to 8 sublinks beneath their listing, which drives down competing listings. For brand related queries it is also common for subdomains to show up.
- related search suggestions - some search results recommend related search queries. this can play a particularly large role in important verticals like health.
- clickworthiness - some listings are easier and more appealing for searchers to click on
- seasonal trends - some searches are particularly seasonal
- universal search / vertical search - some search results feature house content, selected editorial partner content and/or content from vertical databases
- level of competition - if the opportunity cost is too great then it might not be worth the effort to try to rank
- geography - known local sites tend to get a boost in local search results.
- personalization - if people frequently visit your website then Google may promote your pages in subsequent search results.
- keyword tail - in some categories the core keyword has most of the search volume, while traffic is more spread out in other areas. This factor will be covered more in step 4.
Brand
If someone is looking for a specific brand it is hard to outrank the official site or appear more relevant for core brand related search queries, plus people end up visiting the destination brand site on most navigational searches.
Tips:
- An easy way to compete for brand related queries is to rank for reviews, coupons, specific part numbers, accessories, or other related keyword terms that do not force you to compete directly with a company like Dell Computers for the keyword Dell.
- If you are a brand that sells directly consider setting up a policy that prevents affiliates from outbidding you and driving up your costs on your own brand related keywords.
- In some cases it may make sense to bid on your brand related keywords, especially if your brand is generically descriptive in nature (like CreditCards.com).
- If you own a branded web property it helps to create at least one strong subdomain to help drive down any negative publicity and/or competing ads that may arise down the road.
User Intent
Most people who search are looking to research information rather than buying an item, and yet most pay per click ads aim to sell items.
Tip:s
- If a person searches for a research oriented keyword and your listing uses words like compare and reviews in it then the searcher will find your listing more relevant to their needs and be more likely to click on your listing.
- Microsoft offers an online commercial intention tool, which offers insights into search intent.
Paid Search Ads
If paid search ads appear above the organic search results they drive down the organic search results and take away many of the potential clicks. Google is aggressively focused on keeping attention focused on the upper left corner of the search results, and will only display ads on top of the search results if they have high perceived relevancy driven by a high CTR.
Tip: We typically scan search results in groups of 3 or 4. If 3 paid search ads appear above the search results for a keyword you really need to be in the top 3 organic search results to get much traffic.
Sitelinks, Subdomains, & Multiple Listings
When Google believes a query has a good chance of being navigational in nature they may place a list of sitelinks under the first listing. Sitelinks can really drive down competing ads.
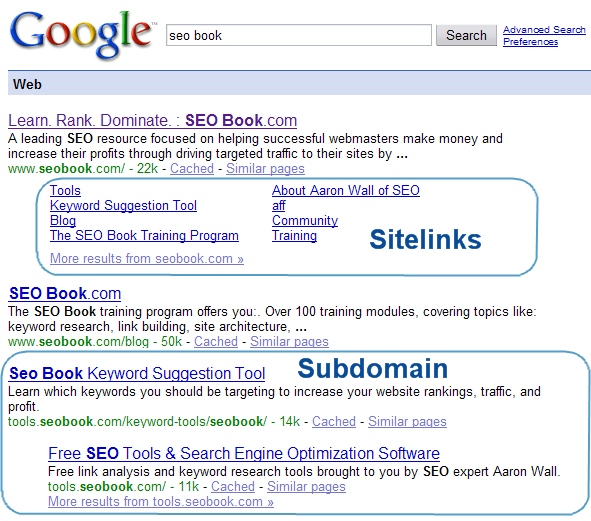
Tips:
- If you have sitelinks for a highly valuable commercial keywords it may also make sense to bid on the related AdWords ads to further reinforce that you are the default market leader in that space.
- You are more likely to get sitelinks if your domain name exactly matches the search words.
- If you resell a brand which has sitelinks and subdomains listed for the core term make sure you target some related keyword tail phrases rather than trying to rank for the core word. Unless your site is exceptionally authoritative or your market is not competitive, for the core keyword you might be better off buying AdWords ads.
- If you own a branded web property it helps to create at least one strong subdomain to help drive down any negative publicity and/or competing ads that may arise down the road.
- For moderately competitive keywords authoritative sites may be able to get a double listing which may double the probability of a searcher clicking on your site since you have 2 listings in the search results and your site is set apart because one of those listings is indented.
Related Search Suggestions
All major global search engines offer suggested related queries in the search results for some search queries. Sometimes they appear at the top of the search results and sometimes they appear at the bottom.
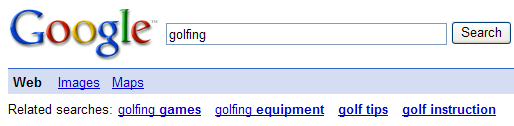
Tip: If core industry related words are too competitive, you can rank for related keywords that search engines recommend. That allows you to tap the traffic flow of the competitive keywords without requiring the authority needed to rank for them.
Clickworthiness
Many people target keywords without understanding search intent. If your listing is more relevant than competing services then people are more likely to click on it.
Tips:
- Search for some of your most important keywords that you rank for and look at how your listing compares to competing listings. Could you make your presentation more unique or relevant?
- When creating new pages on important topics consider the search presentation when crafting your page title, meta description, and filenames.
Seasonal Search Trends
Some keywords grow popular around news items or particular dates.
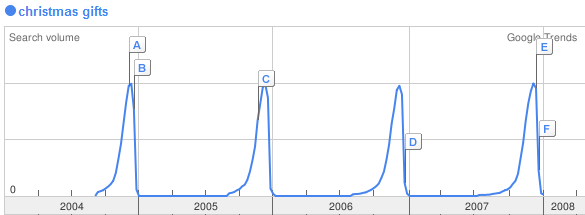
Tips:
- Subscribe to related news publications and blogs to track conversation in your marketplace.
- Use tools like Google Trend to evaluate when search volume picks up for important keywords.
- Promote important seasonal time sensitive offers at least one month before it becomes popular such that when people search for it your site already ranks.
- When using paid search set important seasonal keywords in their own ad groups or ad campaigns and monitor and manage them closely when search volume starts picking up.
Universal Search / Vertical Search
Google owns many vertical properties and sometimes integrates results from editorial partners (in the news vertical) or house content (Google Local, images, YouTube videos, etc.) in their search results. In April of 2008 iProspect released a Blended Search Results Study [PDF].
Tips:
- If Google has placed vertical search results in their organic results or you think there is a good chance they may then optimize your presence in those verticals.
- Ensure your site has editorial, tools, brand, and/or some other value add which still allows you remain a destination as Google pulls more data and value directly into their search results.
Level of Competition
Trying to rank for a competitive keyword in 2008 with a new site may not be feasible unless you have significant capital, significant social currency, and/or great ideas.
Tips:
- If you are on a brand new website ensure you are using appropriate keyword modifiers and are aiming at some long tail keywords your site has the ability to rank for.
- Download SEO for Firefox and watch the associated how to video to understand how to evaluate the competitive landscape of a keyword.
- When you see weak competitors ranking surprisingly well, use competitive research tools to see what else they are ranking for.
Geography
People in different locations see different search results.
Tips:
- If your target market is foreign consider doing at least one of the following
- registering a domain name matching that country
- hosting your site in that country
- register your site as being associated with that country inside Google Webmaster Tools (can be done at the domain, subdomain, or folder level).
- Use this Google Global Firefox extension to quickly look up your rankings.
- If you want to track where you rank over time our Firefox Rank Checker is also worth downloading.
Personalization
People who have seen your site before are more likely to see it ranked well in subsequent search results.
Tips:
- Participate in your community. Make sure you know your market well to use the language that they do, so they come across your site early in the buy cycle.
- Create the type of content that people want to cite.
- Create lots of content that make your site relevant for a wide array of keywords.
- Use a clean and effective site design and show social proof of value so your site is easy to trust and subscribe to.
- Build interactivity and community into your website so people keep coming back to your site.
- Advertise aggressively if it makes sense with your current business model. If you sell something you may further extend your reach via the use of affiliate programs.
Step 4: Tapping the Keyword Tail
The Tail is Long
People search for everything under the sun. When the leaked AOL search data was manually classified into 20 different categories the category with the leading volume was other
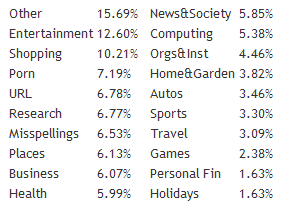
That other is bigger than most people appreciate.
- In a 2004 presentation on Challenges in Running a Commercial Web Search Engine [PDF] Google's Amit Singhal mentioned that out of over 200 million unique daily search queries seen by Google over 100 million are unique.
- On May 16, 2007, at the Searchology event, Google's Udi Manber stated that 20 to 25% of the queries that Google sees in any given day are queries that they have never seen before. Matt Cutts later clarified this data point, saying that it is accurate if you look back through the most recent month's queries.
While earlier research showed more focus on head keywords, in January of 2007 OneStat shared search volume breakdown by number of keywords in the search query for 2 million website visitors. From their data 4 word search queries were more popular than 1 word queries.
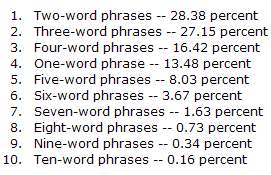
In early 2008 Google's Avinash Kaushik stated that the average Google query consisted of 4 words.
Competitive Research
There are many competitive research tools on the market which show how many keywords a website ranks for. Compete.com Search Analytics also estimates what percent of a site's traffic is driven by each keyword they rank for.
- By comparing the number of keywords you rank for compared to competing sites you can get a good idea how long your keyword tail is compared to their tail.
- By looking at the percentage breakdowns of their top keywords you can find important keywords you forgot to target.
- It may also be helpful to look at competitive research stats for slightly broader keywords and slightly broader websites to look for trends amongst them.
Comparing Search Volumes for Keyword Match Types
Google Traffic Estimator and Microsoft Ad Intelligence allow you to compare the size of the keyword tail to a core keyword. Looking at these ratios and how competitive the search results are for the related keywords can help you determine where to focus your energies.
Tips:
- If head keywords [exact match] have a lot of search volume try to buy a domain name that matches those keywords.
- If keywords have a long tail, create content focused on the tail, especially if few competitors are targeting it.
Compete.com Search Analytics shows keyword distribution estimates for both exact match and broad match versions of keywords. If a site appears low for the exact match version of a keyword but high for the broad match version then they are doing a good job of capturing the keyword tail.
Search Suggestion Tools
Search engines like Google and Yahoo! help auto-complete search queries via services like Google Suggest and Yahoo! Search Suggest. They generally place these recommended keywords in order of popularity / search volume.
Some search results also offer search refinement options that help drive searchers to related search queries.
The Importance of Keyword Modifiers
Many searches that have a long tail associated with them have a number of common modifiers associated with them. By working these modifiers into your content you can rank for a much broader basket of keywords. Here is a XLS spreadsheet of common keyword modifiers and categories.
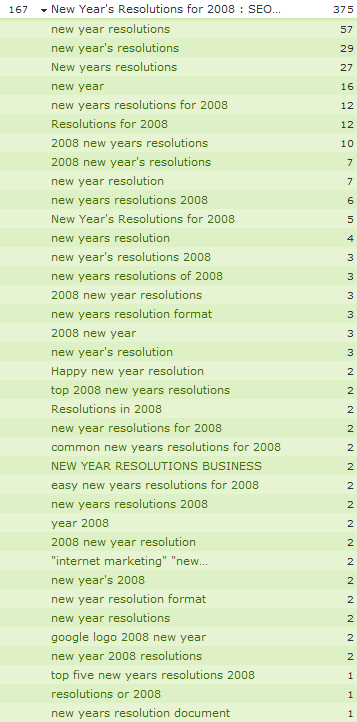
User Generated Content
Some of the highest value web publishing networks have a strong value because they encourage readers to contribute content to their websites. Dozens of product reviews or comments added to a page offers a lot of unique content which helps the page rank for a much wider net of related keywords. Here are stats showing a single blog post ranked for hundreds of unique keywords
Want more keyword tips?
Read our free 14 page training module on keyword research.
Step 5: Improved Monetization via Scale
With more scale you can test and improve monetization faster, be more selective with what customers you are willing to work with, have leverage over suppliers, and/or negotiate direct ad deals that allow you to drastically increase the profits from your website. To put this in perspective...
- Wal Mart can sell a gallon of Vlasic pickles for $2.97.
- If you monetize your website via AdSense, Google is taking a big cut. Simply eliminating them from the transaction may double your earnings.
- Super affiliates can negotiate higher pay outs for conversions.
- If you get enough scale, it may become economical to create your own products based on how receptive your audience is to other offers.
- Brand advertisers pay a premium for engagement and volume. If you are small they may skip you over, but if you have enough volume they will work directly with you.
Step 6: Take Action Today
Thanks for reading this far! Reading this should give you a competitive advantage, but all the above advice is meaningless unless you use it to improve your business.
Want to Join the #1 SEO Training Course?
Join Today
Subscribe today to gain immediate access.
What You Get When You Join
You are only 1 step away from having access to all kinds of SEO goodies, including:
- the top ranked online SEO training program, which includes over 100 training modules, has been well referenced around the world, & is currently being used as course material for accredited college courses in internet marketing.
- the leading SEO community forums where you can interact directly with some of the sharpest minds in search & get your questions answered.
- many high-quality exclusive SEO tools including our Website Health Check Tool, Competitive Research Tool, Duplicate Content Checker, Hub Finder, and the LocalRank tool
Join a True Community of SEO Experts
I've been a paying member since day one. It's been the best $2000 I've ever spent on SEO, SEM, Social Media and general business information.
Community members have very meaningful online success in difficult niches. These personalties combine to produce quite frankly a vital resource for all serious online businesses. - Liam Delahunty
Killer SEO Tools!
Join Today
Subscribe today to gain immediate access.
Need More Information?
Want to learn more? Check out the member tour.